
Structure of a motor neuron. Anatomy of a typical human neuron. Structure neuron , SPONSORED,
How do Neurons Work? Neurons lie adjacent to each other but are not connected. There is a tiny gap between neurons called a synapse. The function of a neuron is to transmit nerve impulses along the length of an individual neuron and across the synapse into the next neuron. The electrical signals transmitted by neurons are called action potentials.
The Neuron External Structure and Classification Interactive Biology, with Leslie Samuel
motor system: The part of the central nervous system that is involved with movement. It consists of the pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems. cerebral cortex: The gray, folded, outermost layer of the cerebrum that is responsible for higher brain processes such as sensation, voluntary muscle movement, thought, reasoning, and memory.
What Are the Major Neurotransmitters? (with pictures)
The presence of the synaptic cleft between the synaptic end bulb of the neuron and the motor end plate of the muscle fiber, means that the electrical signal or action potential, arriving from the central nervous system, needs to somehow transverse (cross) this space.The neuromuscular junction accomplishes this by turning the electrical signal from the nervous system into a chemical signal that.

FileNeuron1.jpg Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(A) Diagram showing a lower motor neuron in the spinal cord and the course of its axon to the muscle. (B) Each motor neuron synapses with multiple muscle fibers. The motor neuron and the fibers it contacts defines the motor unit. Cross units and the α motor neurons themselves vary in size.

What Are Dendrites Structure And Its Functions
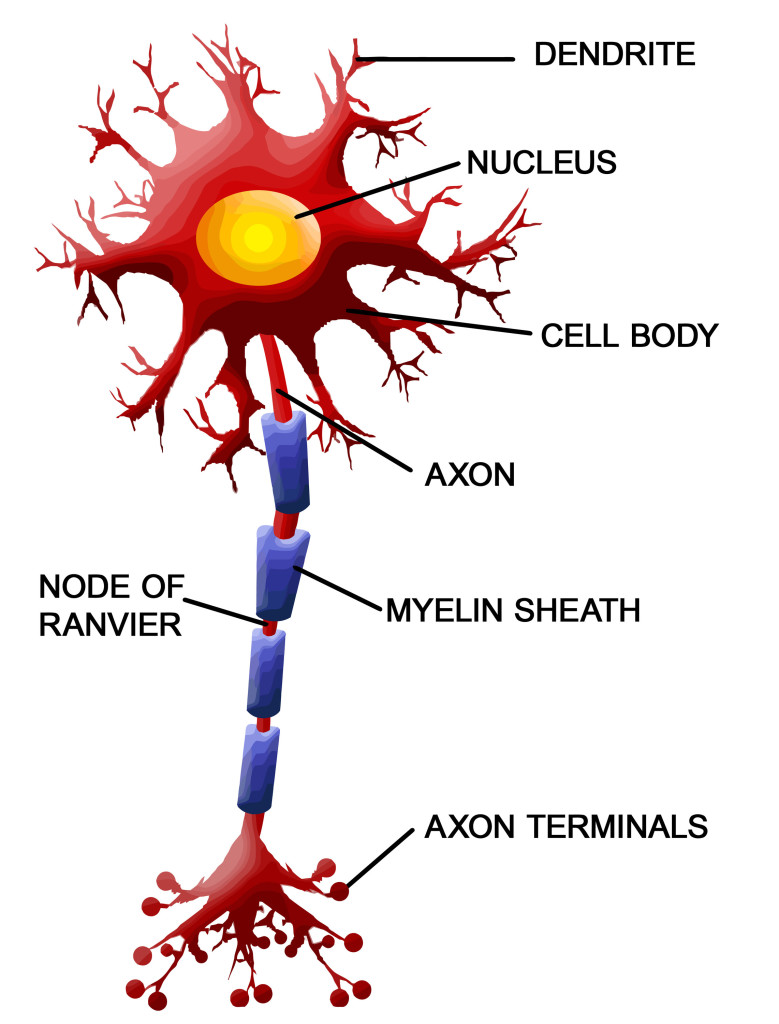
6.5.2 Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron. Figure 6.5.1 - A motor neuron. 6.5.3 State that nerve impulses are conducted from receptors to the CNS by sensory neurons, within the CNS by relay neurons, and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons.

structure of motor neuron. Vector diagram. Include dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon
At the synapse, the firing of an action potential in one neuron—the presynaptic, or sending, neuron—causes the transmission of a signal to another neuron—the postsynaptic, or receiving, neuron—making the postsynaptic neuron either more or less likely to fire its own action potential.

NEURONE SCARICARE
A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. Motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. When these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. This is characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy) and loss of motor function. Motor Neuron.

Draw A Neuron And Label Its Parts Q10 A Draw The Structure Of Neuron And Label Cell Body And
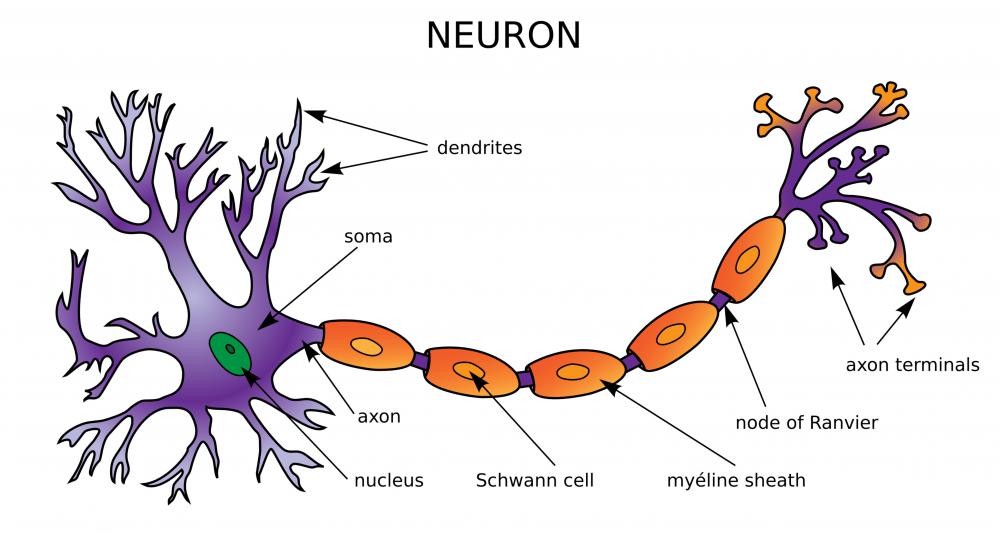
Diagram Of Neuron with Labels Here is the description of human neuron along with the diagram of the neuron and their parts. The neuron is a specialized and individual cell, which is also known as the nerve cell. A group of neurons forms a nerve.
Images 11. Nervous System Basic Human Anatomy
Overall, motor neurons (or motoneurons) comprise various tightly controlled, complex circuits throughout the body that allows for both voluntary and involuntary movements through the innervation of effector muscles and glands. The upper and lower motor neurons form a two-neuron circuit.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg)
Human Biology The Anatomy of Neurons
Let's dive a bit deeper into the functioning of motor neurons as we refer to a neatly labeled diagram. Structure, Function, and Location of Motor Neurons Structure All motor neurons are multipolar neurons. A multipolar neuron has only one axon and densely branched dendrites.

Diagram Of Motor Neurone
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron [1]) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. [2] There are two types of motor neuron.

Motor Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
An Easy Guide to Neuron Anatomy with Diagrams Anatomy Types Function Research Takeaway Neurons, also known as nerve cells, send and receive signals from your brain. While neurons have a lot.

Neurons What are they and how do they work?
The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements.

Motor Neuron
Motor neurons, also known as efferent neurons, are nerve cells responsible for carrying central nervous system signals towards muscles to cause voluntary or involuntary movement through the innervation of effector muscles and glands. Their nerve fibers are considered to be the longest in the human body .

Motor Neuron Disease Neurological Issues Herbal Care Products
Cerebellum - molecular, Purkinje, granular layers. Peripheral nerves - epineurium, perineurium, endoneurium. This article will explain the histology of neurons, providing you with information about their structure, types, and clinical relevance. It will also cover briefly the histological layers of the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Motor Neuron Diagram Neuron Structure and Function_4_ Personal Branding Pinterest
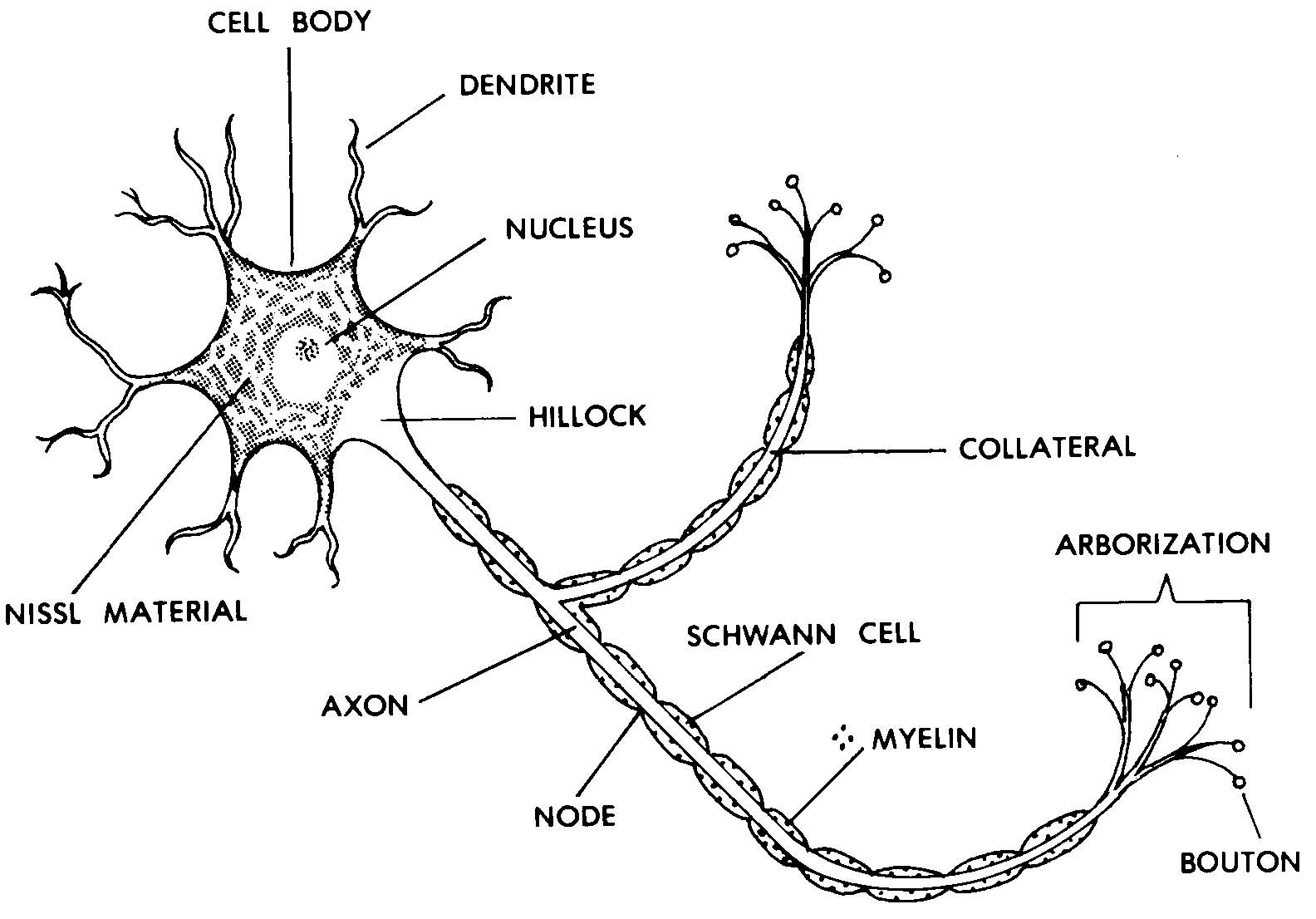
Parts of an Axon. a) Axon hillock - The part of the axon which remains attached to the cell body or soma. b) Myelin sheath - The layer of fatty acid produced from specialized cells called Schwann cells that are wrapped around the axon. c) Nodes of Ranvier - The gaps between the discontinuous myelin sheath that is running along the axon.