Animal Cell Class 9 Ncert / NCERT Class VIII Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure And Cbse
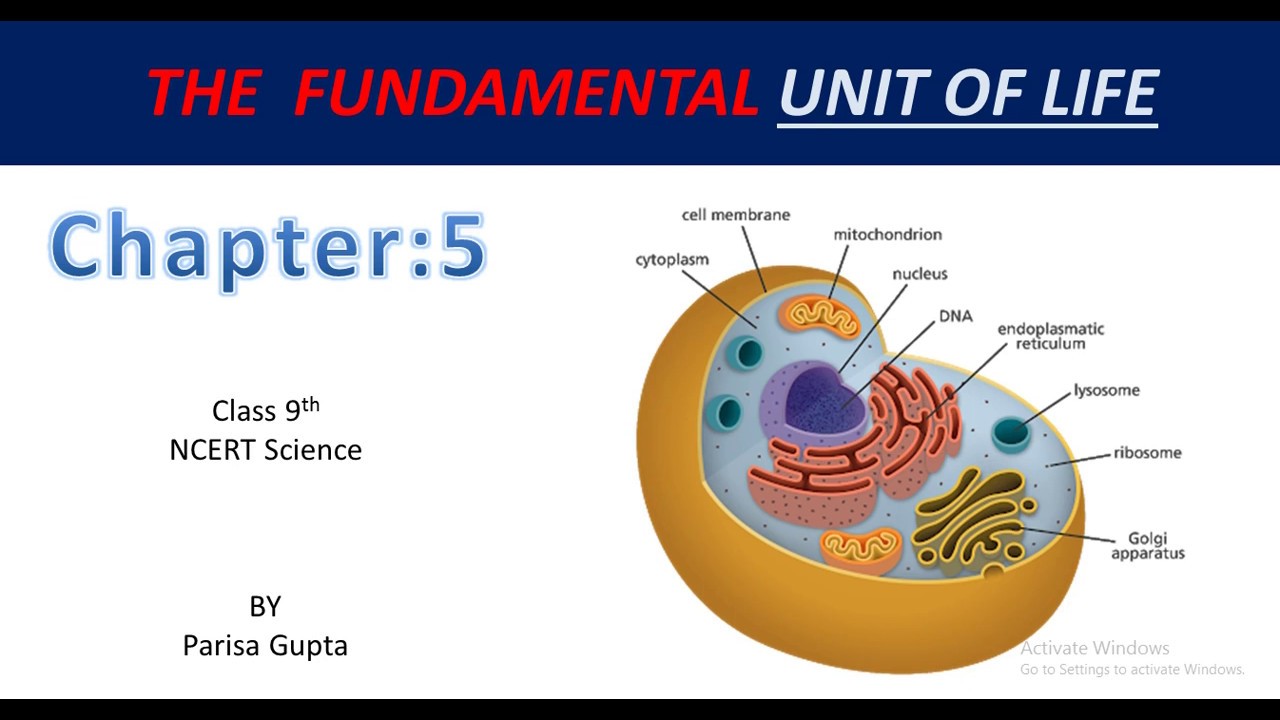
What's in it? In Chapter 5 of Class 9, you are going to learn about the fundamental unit of life which is the cell with the help of concepts, NCERT questions and Extra Questions prepared by the experts at Teachoo. Starting with the concept of the structure of a cell, you will learn about the physical properties of a cell.

Selina Solutions Class 9 Concise Biology Chapter 2 The Unit of Life Download Free PDF
Welcome to Class 9 The Fundamental Unit Of Life notes Notes for Chapter 15.The topics in this page are Discovery of cell ,Cell Theory,Shape, size and number of cells,Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells,Structure of cell, Cell Membrane,Cell Wall,Cell organelles and Nucleus. This is according to CBSE and the NCERT textbook.

The Structural Organisation of a Cell/Class 9 YouTube
Answer: Fungi, plants, animals. (Any one) Question 8. What is active transport? Answer: The movement of molecules across a membrane in cells against a concentration gradient with the help of ATP units is called active transport.
CLASS 9 BIOLOGYSolved Test Paper THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE CBSE ADDA
Biology Biology Article Cell Organelles Cell Organelles More than 8.7 million species are living on the planet. Every single species is composed of a cell and it includes both single-celled and multicellular organisms. The cells provide shape, structure and carry out different types of functions to keep the entire system active.
Easy way_ Difference between Plant cell and animal cell. Class 9. recorded lecture on zoom
The cell membrane is the outermost covering of an animal cell. It encloses the other components of the cell , such as the nucleus and the organelles. It is also known as the Plasma membrane . The cell membrane is flexible and its shape can be changed as needed. The plasma membrane is made of substances called lipids and proteins which lend it.

How to draw plant cell for class 9 / Plant cell diagram step by step /पादप कोशिका की संरचना का
Answer: A cell is capable of independently carrying out all necessary activities of life. So, they are called basic or functional unit of life. Formulae Handbook for Class 9 Maths and Science Educational Loans in India Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook - Page 61 Question 1.

CELL AND ITS ORGANISATION//CELLA BRIEF INTRODUCTION AND IT'S TYPE CLASS IX CBSE / OAV YouTube
Biology Biology Article Cells Cells 1,77,257 Cells are the basic, fundamental unit of life. So, if we were to break apart an organism to the cellular level, the smallest independent component that we would find would be the cell. Explore the cell notes to know what is a cell, cell definition, cell structure, types and functions of cells.

Plant And Animal Cell Class 9 NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Chapter
The type of cell that accounts for 90-95 percent of your skin are keratinocytes. Instead of being round and blob-like, their shape has a flake-shape than anything else, creating a mosaic of skin. They grow and divide in the basement membrane, a thin layer that separates your epidermis from your dermis. There they push toward the top of your skin.

Plant Cell Diagram Labeled Class 9 Labeled Functions and Diagram
Cell Shape. Usually, the cells are round, elongated or spherical. There are also some cells which are long and pointed on both the ends. Such cells exhibit spindle shape. In some cases, the cells are very long. Some may be branched like the neuron or the nerve cell. The nerve cell transfers and receives messages.

draw a diagram of animal cell for class 9 Brainly.in
June 15, 2022 by Sastry CBSE The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Notes - Here We have provided summary and revision notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 5. This CBSE notes contains CBSE Key Notes, CBSE Revision Notes, Short Key Notes, images, diagrams of the complete Chapter 5 titled The Fundamental Unit of Life of Science taught in class 9.

How to draw animal cell labelled diagram Animal cell diagram for class 9,10 and 11 YouTube
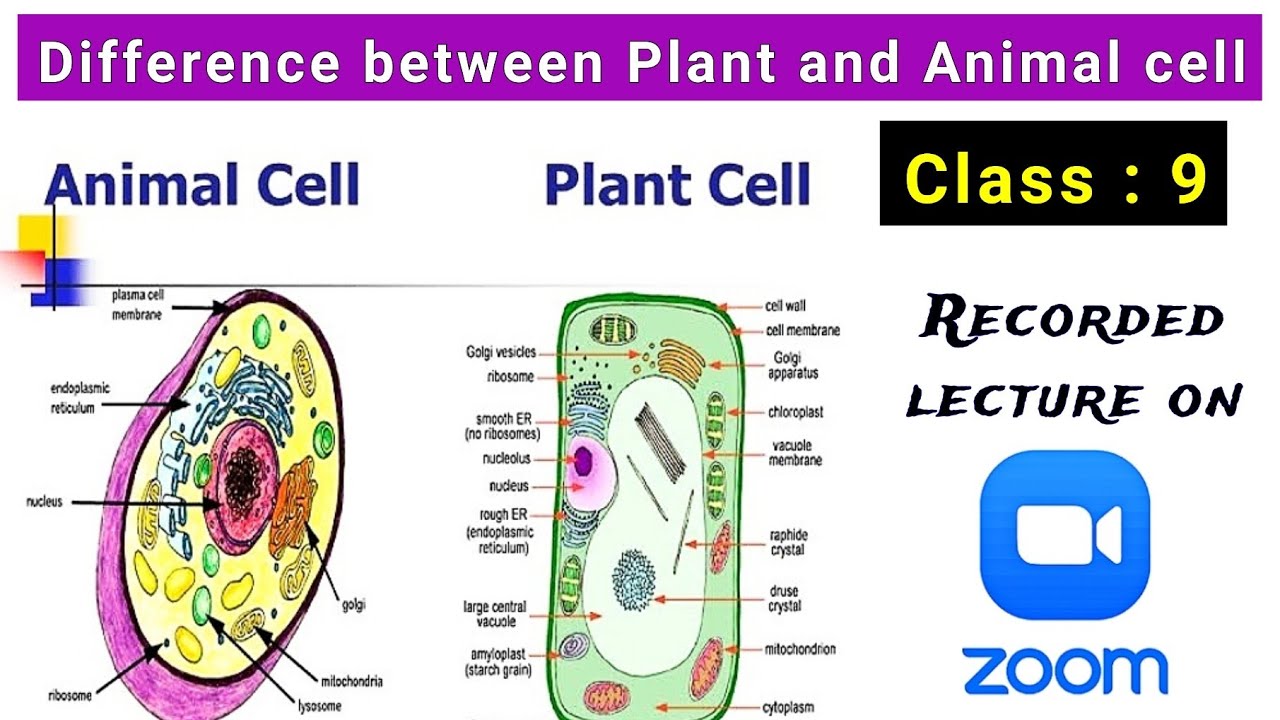
Study Material and Notes of Ch 5 The Fundamental unit of Life Class 9th Science Topics in the Chapter • Introduction • The cell theory → Types of organisms → Types of cells • Difference between Animal cell and Plant cell • Diffusion • Osmosis • Hypotonic or Hypertonic or Isotonic solution • Plasma membrane or Cell membrane

Class 9 Biology notes for Chapter 6 Tissues and important points
The Class 9 Science Notes for The Fundamental Unit Of Life - Cell include concept mapping and revision notes for all topics taught in the class 9 Science textbook in this particular unit. In addition there are important questions for class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit Of Life - Cell - very short, short, long answer type for you to practise.

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell for Class 9 CBSE Class Notes Online Classnotes123
CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life helps you understand how the different cells work, what they are made of and what are their functions. You will learn about the animal cells and their components along with plant cells and their functions. Studying this chapter will help you understand advanced concepts in Biology.

Animal Cell Class 9 What is a Animal Cell, Structure, Function & Types
The Fundamental Unit of Life Cell Class 9 One-Shot Easiest Lecture | Class 9 Science | 2021-22Topics - 1) The Fundamental Unit of Life2) The Fundamental Unit.

Difference Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell Class 9 Chapter 5 YouTube
cell and are called unicellular organisms while others, like us, composed of many cells, are called multicellular organisms. 8.1 WHAT IS A CELL? Unicellular organisms are capable of (i) independent existence and (ii) performing the essential functions of life. Anything less than a complete structure of a cell does not ensure independent living.

CELL CLASS9 ICSE EASY EXPLANATION YouTube
Solution: Cells form the structure of an entity. A group of cells form a tissue, further an organ and ultimately an organ system. They perform fundamental functions and life processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion etc., in both unicellular and multicellular entities. They perform all the activities independently.